Rabbit rickets
Rabbit rickets (ravirial haemorrhagic disease in rabbits) is more prevalent in winter and the incidence rate is greatly increased. It may be that rabbits in autumn breed gradually become older in the winter. Since immunization work is not done well, they have become susceptible rabbits, plus winter temperatures. Low, outside the virus is not easy to die, the acquisition of liquidity increased rabbit products, pathogens spread more easily, resulting in a significant increase in the incidence rate. In order to prevent epidemic prevention of rabbit plague, it is necessary to purchase a reliable quality rabbit inactivated rabbit viral haemorrhagic vaccine (rabbit cricket vaccine) or rabbit viral haemorrhagic disease and multi-killing pasteurellous disease inactivated vaccine (rabbit).瘟 Papilla double seedlings) immunization according to immunization procedures.
In the event of rabbit rickets, rabbits were immediately inactivated with a rabbit viral haemorrhagic disease and the entire group of threatened rabbits over the age of 30 days was vaccinated. Four to five milliliters of subcutaneous or intramuscular injections were administered to each rabbit. At the same time, we must strengthen disinfection and take measures as soon as possible.
Respiratory disease
In order to avoid the cold, take appropriate measures to keep warm, such as closing doors and windows, warming or using plastic sheeting to close the rabbit house, cover the straw and so on. Therefore, the ventilation in the house was poor, the concentration of harmful gases and humidity increased, and the incidence of respiratory diseases in rabbits generally increased. Within 7-10 days after ventilation in the house changed, the incidence of intranasal rhinitis increased significantly. With the prolongation of time, the symptoms of rhinitis became more pronounced. The incidence of pneumonia in puppies also increased. Acute pneumonia and purulent infection in rabbits. Pneumonia, lung abscess, and other diseases are increasing, and the mortality rate in rabbits has increased. Therefore, the following comprehensive measures are recommended.
1. Improve environmental conditions. When temperature conditions permit, try to ensure that the rabbithouse is well ventilated and dry. In winter, the climate is cold. Generally, as many rabbit houses are closed, forced ventilation should be considered. The excrement should be promptly removed to reduce the generation of harmful gases. Frequent spraying with disinfectant solution in rabbit houses reduces the density of pathogens and the amount of dust in the air.
2. Strictly control the condition. In the context of improving environmental conditions, a small number of diseased rabbits should be isolated and treated or eliminated in time to avoid spreading the disease. Rhinitis more serious or long-lasting should be firmly eliminated.
3. Immune injection. The pathogenic bacteria of infectious rhinitis can cause pneumonia in rabbits and cause death. Therefore, in order to reduce mortality, the vaccine should be injected. Rabbit inactivated pasteurellosis vaccine or pasteurosis and Borrelia double vaccine vaccine can be used for injection. Although these vaccines cannot be used to solve the problem fundamentally, the incidence of some respiratory diseases can be reduced. mortality rate.
medical treatement. For diseased rabbits, which are more likely to occur and are unlikely to be completely eliminated, proper treatment should be given. The use of enrofloxacin, gentamicin and other drug injection therapy. Each rabbit was intramuscularly injected 0.5-1.0 mL/time, once or twice a day for 5-7 days. If the disease is severe in winter, drugs such as ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, etc. can also be added to the feed and the drug can be discontinued after 4-5 days of continuous use.
Dermatomycosis
Because of the closed rabbit house in winter, with poor ventilation and high relative humidity, the dermatophytosis of rabbit skin is prone to outbreak and the incidence is high. Due to the low temperature and poor resistance of rabbits, it is easy to infect other diseases and cause serious economic losses. For the prevention of dermatomycosis in rabbits, the following measures can be taken.
prevention. Within 2 days after birth, all rabbits were soaked with soaking agent for 1 time. Twenty-five days of pups were injected once with injection drug, 0.5-1 ml per rabbit. The pregnant female rabbits were injected subcutaneously with 2 ml of injection drug 5-7 days before delivery, and injected again 5-7 days after delivery.
treatment. The incidence of pups in the 10-20 days of age, one-time injection of drugs 0.5-1ml. Those who have severely healed will repeat the drug once. Young rabbits: Each rabbit was injected subcutaneously with 1-2 ml of the drug and repeated once every 7-10 days. Onset female rabbits were injected subcutaneously with 2 ml of the drug and repeated once every 7-10 days.
Environmental disinfection. There are a large number of pathogens in the environment of rabbits in the pathogenesis, which is a potential threat to the onset of rabbit farms. It is necessary to strictly disinfect rabbit houses, cages, utensils, and home environments. Disinfection can be flame available (where flame disinfection can be used as far as possible using flame disinfection), chemical drugs such as 2% fire alkali, chlorine disinfectant, peracetic acid, etc., and 15 to 20% lime water can be used for large areas ( Fresh) Repeatedly sterilized.
Disinfection in vitro. With drug treatment and large-scale disinfection of the entire site, animals, including rabbits, pigs, dogs, cats, etc., in this field are each given a medicated bath to eliminate the pathogens carried by the animals' body and coat. Disinfectants can be used chlorine disinfectant and other drugs that can kill fungi. Medication bath can be used to increase the concentration. Care should be taken to choose a medicated bath at temperatures above 25°C.
To eliminate fungal disease, you must pay attention to the following matters.
1, the audience action: due to the onset of the rabbit environment and the rabbit itself is generally infected, only effective treatment of symptomatic rabbits, but the incidence will continue, so take the whole field of unified action, to take all measures, including prevention , treatment, environmental disinfection and surface disinfection.
2, long-term adherence: Adhere to medication prevention and treatment and environmental disinfection and surface disinfection, greatly reduce the incidence, inhibit the proliferation of bacteria, reduce the chance of transmission, can be effective in the short term, but because of the pathogen in rabbit environment A long time is a big hidden danger. It must be adhered to and used for a long time.
3. Regeneration of rabbits: It is difficult to eliminate the carriers of the diseased rabbits, and it is necessary to select superior rabbits from the offspring that have not been diseased after adopting preventive measures to gradually replace the original rabbits.
4. Be cautious about introduction: Remember that it is not easy to introduce exotic breeds of rabbits and other animals in order to avoid doing anything.
Coccidiosis
Many people believe that rabbits do not suffer from coccidiosis in the winter, but this is not the case. In recent years, some rabbit farms have neglected winter to prevent coccidiosis in rabbits, leading to an outbreak of coccidiosis in rabbits. Although the outside temperature in winter is very low, the temperature and humidity in the rabbit house are still suitable for the development of coccidial oocysts, and there are still more mature coccidia oocysts in the rabbit house and female rabbits. These matured After the oocysts of the coccidia are engulfed by the pups, the infection will occur, and the disease may occur or die when the infection is severe. Therefore, in winter rabbits, anticoccidial drugs should be added in the feed in a common preventive measure.
When rabbit coccidiosis occurs, the available pre-mixed Kjelly premix, according to the amount of instructions plus 5-6 times, continuous medication 2-3 days, to be controlled after the onset of the disease to normal prevention, can also use the word Coccidiosis powder for treatment.
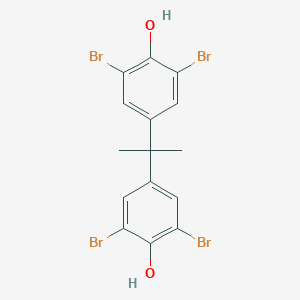
Tetrabromobisphenol A CAS No.79-94-7
Tetrabromobisphenol A Basic Information
Product Name: Tetrabromobisphenol A
CAS: 79-94-7
MF: C15H12Br4O2
MW: 543.87
EINECS: 201-236-9
Mol File: 79-94-7.mol
Tetrabromobisphenol A Structure
Melting point 178-181 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 316 °C
density 2.1
storage temp. 2-8°C
solubility Insoluble
form neat
tetrabromobisphenol a,tetrabromobisphenol a msds,tetrabromobisphenol a (tbbpa),tetrabromobisphenol a bis (2 3-dibromopropyl ether),tetrabromobisphenol a bis
ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com